Options (Find Duplicate Files)
These options pertain to the Find Duplicate Files functionality of FolderMatch.
Include Subfolders: To include the subfolders of the selected folder(s) in your search, select YES for this option.
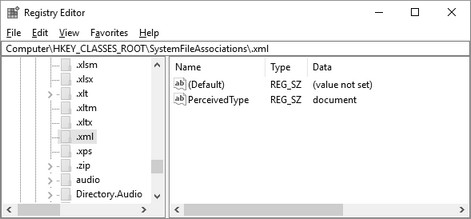
The choices are: •All File Types •Application •Audio •Document •Image •Text •Video Note:
The software program that creates the files having a particular extension is ordinarily the one that registers the perceived type for the extension. Changing these settings might impact your system. |
•Names Match •Sizes Match •Last Modified Date/Times Match •Contents Match
File timestamps can be a little unreliable to use as duplicate criteria due to how the different versions of Windows handle timestamps. Two files can be identical yet have differing dates. Don't put too much stock in differing timestamps.
The program requires you to select either the Names Match or the Sizes Match criteria as an initial selection. You can then add any of the other criteria. |
•Ignore System Files •Ignore Hidden Files •Ignore Files in Windows Folder Tree
Additional Ignore options include: •Ignore Temporary Files •Ignore Zero Byte Files
A Temporary file (or temp file) is a file created by a program to hold information temporarily. After the program is closed, it should delete the temporary file. But sometimes this does not happen. Microsoft Windows and Windows programs often create a TMP file as a temporary file. If a temp file is in use, you don't want to remove it. If it's old and should have been removed but wasn't, it should be safe to remove it.
Zero Byte files are files whose size is zero bytes; they contain no contents. These files do not concern most users since they are not taking up any hard disk space.
FolderMatch automatically ignores two other groups of files: files in the Recycle Bin and files in the FM_DUPES folder. You cannot change this behavior. |
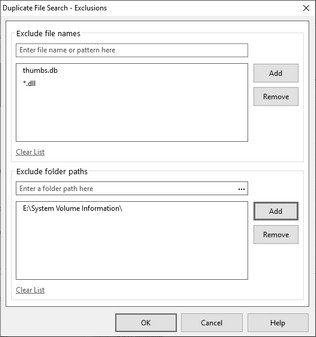
Press one of these buttons to bring up a window where you can enter files and folders to include or exclude from the search. For files, you may enter a complete file name, like "thumbs.db" or you may enter a File Pattern using the wildcard characters * ? like "*.dll". For folders, enter the entire folder path or select a folder by clicking on the three dots
Enter a file name or folder path and press the Add button to add the item to the list. To remove an item from a list, select the item and press the Remove button. To remove all items from a list, click on the Clear List link.
For a discussion of file patterns see the help file topic on Include/Exclude Filters. Only the portion of that topic which deals with file patterns is applicable to the find duplicate files feature though. |
|
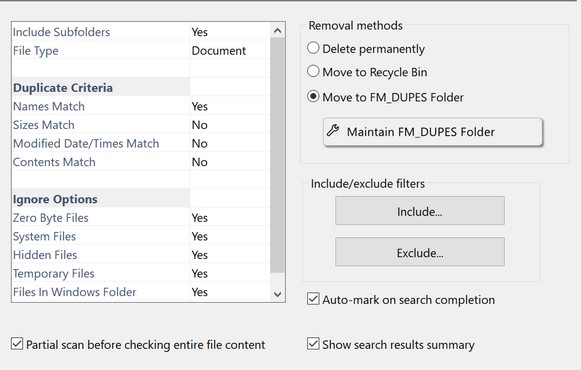
The program can remove duplicate files in several ways. It can move the files to another folder, delete the files permanently, or move them to the Windows Recycle Bin. These three options are the Removal Methods. The safest removal method is to move the file to another folder. This way, you can quickly restore it if needed. The program moves the files to a folder called FM_DUPES.
The FM_DUPES folder is a subfolder of the FolderMatch local application data folder. When the program moves a file to the FM_DUPES folder, it keeps the original path information as part of the moved file's new path. For example, if the file’s original specification was “C:\My Stuff\My Docs\Resume.doc”, the file’s new specification will be “C:\…\FM_DUPES\C\My Stuff\My Docs\Resume.doc”. The highlighted portion of the new file path shows the original path of the file. This makes it clear to see where a file came from and allows you to restore the file easily. Click on the Maintain FM_DUPES Folder button to go to the Maintain DUPES folder window to interact with the FM_DUPES folder and its contents. This window offers the easiest way to restore moved duplicate files.
The Move To Recycle Bin option is also relatively safe. You can restore files removed in this way using the Recycle Bin’s built-in functionality. You should note, however, that Windows does not move files on removable or network drives to the Recycle Bin; it deletes them permanently. So, if you remove duplicates from either of these drive types, using this removal method, know that you won’t be able to restore them. This behavior is per Microsoft Window’s design - FolderMatch has no control over this.
The Delete Permanently option is very dangerous and is one you should rarely use. You cannot restore files removed in this manner without the aid of an undelete utility. |
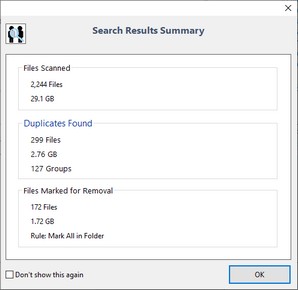
See the Mark Files window topic for more information about the rules. |
Check
|
|